IP Address Management (IPAM)
Effective management of IP addresses is essential for maintaining a well-organized and efficient network infrastructure. IP Address Management (IPAM) solutions offer a comprehensive approach to simplify the complex task of IP address allocation, tracking, and administration. In WISPGate, we will explore the concept of IP Address Management and how it can benefit your organization by enhancing network reliability, security, and scalability.
Benefits of IPAM:
- Efficient IP address allocation and tracking: IPAM automates the process of assigning and monitoring IP addresses, eliminating manual errors and ensuring optimal resource utilization.
- Enhanced network reliability: Proper IP address management prevents conflicts, subnet overlaps, and IP exhaustion, leading to a more stable and reliable network environment.
- Streamlined network operations: IPAM provides centralized control and visibility over IP addresses, simplifying network administration tasks, troubleshooting, and planning.
- Improved security: IPAM solutions enable proactive identification and mitigation of security risks, such as unauthorized IP address usage or IP spoofing attempts.
- Scalability and future-proofing: With IPAM, network expansion, and growth can be easily accommodated by efficiently managing the IP address space and planning for future requirements.
Configuring IPAM:
- Navigate to Networking
- Select IPAM
- Click the Add Network button
- Enter the title of the Network (eg. Sub_Lastmile) Choose address type (IPV4 or IPV6)
- All devices = The subnet will be accessible and available on all devices within the network.
- First Hotspot = referring to the initial device that operates the hotspot subnet
- NewNAS = devices with the capability to act as Sharper, Service Providers, NAT Providers, and Hotspots.
- Second Hotspot = refers to the second device that operates the hotspot subnet.
Select Pool Type as
- CGNAT, also known as Carrier-Grade NAT, is a form of Network Address Translation employed by internet service providers (ISPs) to offer internet connectivity to their customers. Its function involves enabling the sharing of a single, public IP address among multiple customers.
- Last Mile IP Addresses are unique identifiers (IPs) assigned to the endpoint device of subscribers. It serves as the gateway for connectivity and enables smooth access to the internet and online services. With a Last Mile IP Address, subscribers experience consistent performance, personalized identification, and simplified network troubleshooting.
- Public addresses are your public IP blocks, which you can administer within the IP Address Management (IPAM). Public IP addresses, being globally unique, are allocated to devices directly connected to the internet. (Public IP addresses) are globally unique addresses assigned to devices.
- Suspension IPs are utilized by ISPs to temporarily limit or suspend internet access for subscribers. This action is taken in response to security concerns, policy violations, lack pf payment, or other situations that require restricting network connectivity. For instance, if a subscriber’s data package is exhausted, the ISP may suspend their internet access and redirect them to a landing page to provide information about the situation.
- WAN subnets form an essential component of expansive networks that go extensive across geographic regions. These subnets facilitate the seamless transmission of data and information among diverse locations, linking distant offices, data centers, and remote sites. Utilizing routers and other networking devices, WAN subnets efficiently route data packets across the wide area network, guaranteeing dependable and secure communication.
- Management subnets serve as dedicated subnets designed specifically to oversee and control network devices like routers, switches, and firewalls. These subnets are separate from regular user traffic and offer a secure environment that enables network administrators to efficiently manage and configure devices.
- Excluded IPS These IPs remain unallocated to any devices within the network. Think of these addresses as gateways, or a range of reserved addresses designated for specific purposes. You can add many excluded IPs as per your desire.
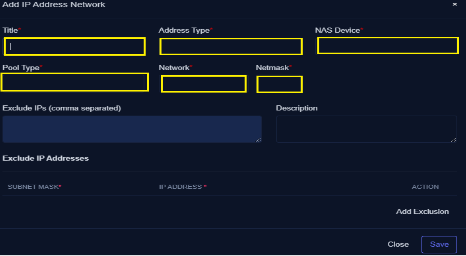
- Enter the Network address (eg: 10.0.0.0)
- Enter the Netmask (eg: CIDR of 24)
- All excluded IPs will be shown in the Excluded IPs (separated by commas)
- Add a brief description for reference purposes. (Not mandatory but recommended)
- Save the Network