NAT (Network Address Translation)
NAT is an essential component in networking that facilitates communication among devices across various networks. It serves as a fundamental technology, enabling multiple devices to utilize a single IP address (mostly a public IP), effectively preserving the scarce pool of available IP addresses. WISPGate allows you to create NAT in many forms as follows:
Generic NAT: Generic Network Address Translation (NAT) is a commonly used technique in networking that allows devices on a private network to communicate with devices on a public network using a shared IP address. It provides a means of conserving IP addresses by allowing multiple devices to share a single public IP address. Generic NAT operates by translating the source IP address and port numbers of outgoing packets and maintaining a translation table to route the incoming responses back to the appropriate devices on the private network.
Creating a Generic NAT:
- Click the Add Natting button
Basic Information
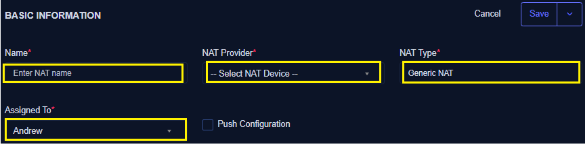
- Enter the name of NAT (*)
- Select NAT Provider (Ensure you have previously created a NAT device under Device) (*)
- Select NAT Type as Generic NAT (*)
- Assign to (*)
- Check the Push configuration checkbox to apply or activate the NAT upon creation (saving)
Generic NAT:

Choose the desired subnet (create subnets from IPAM) Enter WAN IP (consider WAN IP as a public IP) Save the entry.
One-to-One NAT: One-to-One NAT, also known as static NAT, is a specific form of Network Address Translation where each private IP address is mapped to a corresponding public IP address. In this configuration, the translation is one-to-one, meaning each device on the private network has a unique public IP address. One-to-One NAT is often used in scenarios where specific devices or servers within the private network need to have direct public IP accessibility.
Creating a Generic NAT:
- Click the Add Natting button
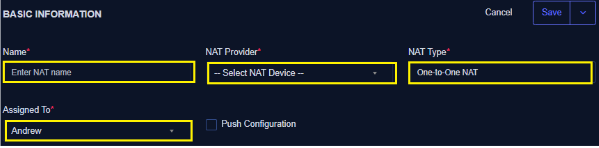
Basic Information
- Enter the name of NAT (*)
- Select NAT Provider (Ensure you have previously created a NAT device under Device) (*)
- Select NAT Type as One-to-One (*)
- Assign to (*)
- Check the Push configuration checkbox to apply or activate the NAT upon creation (saving)
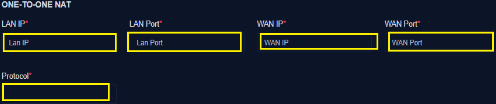
- Enter the specific LAN IP (*)
- Enter the desired LAN Port (*)
- Enter the specific WAN IP (*)
- Enter the desired WAN Port (*)
- Enter desired Network Protocol (*)
NetMap:
NetMap is a specialized form of NAT that allows for the translation of IP addresses on a network while preserving the original port numbers. Unlike traditional NAT techniques that modify both the IP address and port numbers, NetMap maintains the original port information, which can be beneficial for applications that rely on specific port configurations. NetMap selectively translates only the IP addresses while keeping the ports intact.
Creating a NetMap NAT
Basic Information
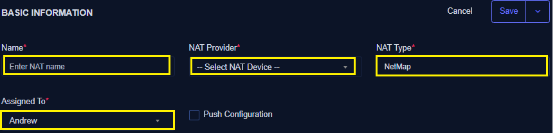
- Enter name of NAT (*)
- Select NAT Provider (Ensure you have previously created a NAT device under Device) (*)
- Select NAT Type as NetMap (*)
- Assign to (*)
- Check the Push configuration checkbox to apply or activate the NAT upon creation (saving)
NetMap
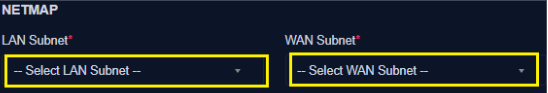
- Enter the LAN Subnet (*)
- Enter the WAN Subnet (*)
CGNAT
CGNATCarrier-Grade NAT used by internet service providers (ISPs), allows the sharing of a single public IP address among multiple customers, providing internet connectivity.
Creating a CGNAT
Basic Information
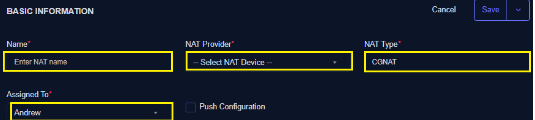
- Enter name of NAT (*)
- Select NAT Provider (Ensure you have previously created a NAT device under Device) (*)
- Select NAT Type as CGNAT (*)
- Assign to (*)
- Check the Push configuration checkbox to apply or activate the NAT upon creation (saving)
CGNAT:
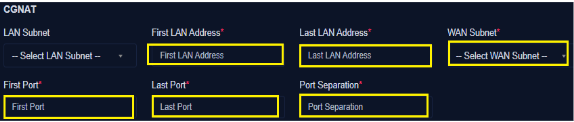
_ Select Subnet (Subnets can be created under IPAM
- Enter First LAN Address (*)
- Enter Last LAN Address (*)
- Select WAN Subnet (*)
- Enter First Port (*)
- Enter Last Port (*)
- Enter Port Separation (*)
Port Forwarding:
Port forwarding, also known as port mapping, is a networking technique that involves the redirection of network traffic from one IP address and port combination to another. It is often used in conjunction with NAT to allow inbound connections from external networks to reach specific devices or services within a private network.
Creating NAT for Port Forwarding
Basic Information
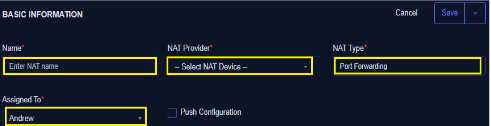
- Enter the name of NAT (*)
- Select NAT Provider (Ensure you have previously created a NAT device under Device) (*)
- Select NAT Type as Port Forwarding (*)
- Assign to (*)
- Check the Push configuration checkbox to apply or activate the NAT upon creation (saving).
Port Forwarding
- Enter WAN IP (*)
- Enter WAN Port
- Enter LAN IP (*)
- Enter LAN Port
- Enter Protocol