IP Address Management (IPAM)
Efficient IP address management lies at the heart of every reliable and secure network. WISPGate delivers a powerful and intuitive IP Address Management (IPAM) system that helps network administrators to centrally allocate, track, and manage IP addresses with accuracy and ease. This solution ensures smooth operations, strengthens network security, and supports effortless scalability.
What is IPAM?
IP Address Management (IPAM) is a centralized solution used to plan, track, and manage IP address usage within a network. It plays a critical role in ensuring that every device on the network is assigned a unique IP address without conflicts, while also simplifying the management of growing and dynamic environments. The core functions of IPAM include:
- Centralized IP Management
IPAM provides a unified platform to maintain an organized inventory of all IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, subnets, and their associated metadata. This eliminates the need for scattered spreadsheets and manual record-keeping. - IP Allocation and Tracking
It enables the automated assignment of IP addresses to devices, preventing duplication, conflicts, and errors. Administrators can easily monitor which IPs are in use, reserved, or available. - Subnet Management
IPAM helps design and manage subnet structures efficiently, allowing for better capacity planning, utilization, and segmentation of the network. - Integration with DNS & DHCP
IPAM allows the integration with DNS and DHCP services to ensure that IP address assignments and hostname resolutions are coordinated automatically, reducing the chance of misconfigurations. - Auditing & Reporting
IPAM tracks changes in the IP address space over time, offering detailed logs and usage patterns. These features are essential for troubleshooting, monitoring, and maintaining compliance with security policies or regulations. - Automation
Automating key processes such as IP address provisioning, subnet allocation, and capacity alerts, IPAM reduces administrative overhead and enhances operational efficiency.
Why It’s Good to Use IPAM
Implementing IPAM solution offers numerous benefits that go beyond just tracking IP addresses. It enhances efficiency, reduces risk, and prepares your network for growth. Here’s why adopting IPAM is a smart move:
- Avoids IP Conflicts – IPAM helps eliminate issues like duplicate IP assignments or subnet overlaps, which are common causes of network downtime. With automated IP tracking and allocation, conflicts are detected and prevented before they disrupt operations.
- Saves Time and Reduces Errors – Manual methods such as spreadsheets are prone to human error and are difficult to maintain. IPAM automates these processes, significantly reducing the chances of mistakes and freeing up administrators to focus on more strategic tasks.
- Scalability – As networks grow and become more complex, IPAM makes it easy to scale without losing control. It enables structured expansion, allowing you to manage thousands of IP addresses, subnets, and devices efficiently.
- Improves Security – Continuously monitoring IP usage, IPAM helps detect unauthorized devices or suspicious activities. This proactive visibility strengthens your network security and reduces the attack surface.
- Supports Compliance – IPAM maintains detailed logs, change histories, and documentation necessary for audits and compliance with industry regulations, making it easier to demonstrate proper network management practices.
- Enables Automation – IPAM integrates with DNS, DHCP, and other systems to support end-to-end automation. This reduces manual workload, enhances speed, and ensures consistent configurations across your network infrastructure.
Configuring IPAM:
- Navigate to Quick Create
- Select Add IPAM
- Click the Add Network button
- Enter the title of the Network (eg. Sub_Lastmile)
- Choose address type (IPV4 or IPV6)
- All devices = The subnet will be accessible and available on all devices within the network.
- First Hotspot = referring to the initial device that operates the hotspot subnet
- NewNAS = devices with the capability to act as Sharper, Service Providers, NAT Providers, and Hotspots.
- Second Hotspot = refers to the second device that operates the hotspot subnet.
Select Pool Type as
* CGNAT, also known as Carrier-Grade NAT, is a form of Network Address Translation employed by internet service providers (ISPs) to offer internet connectivity to their customers. Its function involves enabling the sharing of a single, public IP address among multiple customers.
* Last Mile IP Addresses are unique identifiers (IPs) assigned to the endpoint device of subscribers. It serves as the gateway for connectivity and enables smooth access to the internet and online services. With a Last Mile IP Address, subscribers experience consistent performance, personalized identification, and simplified network troubleshooting.
* Public addresses are your public IP blocks, which you can administer within the IP Address Management (IPAM). Public IP addresses, being globally unique, are allocated to devices directly connected to the internet. (Public IP addresses) are globally unique addresses assigned to devices.
* Suspension IPs are utilized by ISPs to temporarily limit or suspend internet access for subscribers. This action is taken in response to security concerns, policy violations, lack pf payment, or other situations that require restricting network connectivity. For instance, if a subscriber’s data package is exhausted, the ISP may suspend their internet access and redirect them to a landing page to provide information about the situation.
* WAN subnets form an essential component of expansive networks that go extensive across geographic regions. These subnets facilitate the seamless transmission of data and information among diverse locations, linking distant offices, data centers, and remote sites. Utilizing routers and other networking devices, WAN subnets efficiently route data packets across the wide area network, guaranteeing dependable and secure communication.
* Management subnets serve as dedicated subnets designed specifically to oversee and control network devices like routers, switches, and firewalls. These subnets are separate from regular user traffic and offer a secure environment that enables network administrators to efficiently manage and configure devices.
Excluded IPS
These IPs remain unallocated to any devices within the network. Think of these addresses as gateways, or a range of reserved addresses designated for specific purposes. You can add many excluded IPs as per your desire.
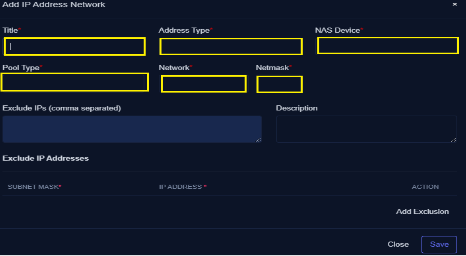
- Enter the Network address (eg: 10.0.0.0)
- Enter the Netmask (eg: CIDR of 24)
- All excluded IPs will be shown in the Excluded IPs (separated by commas)
- Add a brief description for reference purposes. (Not mandatory but recommended)
- Save the Network